17 June 2014 at 14:00 - "Formal Analysis of Security and Safety in Distributed Systems"
Speaker:
Panagiotis Katsaros, Assistant Professor
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Abstract:
Concurrency, communication and information flow in distributed systems are sources of design errors that affect the systems' trustworthiness. We present our research activities on formal analyses for various aspects of security and safety. Security specifications of systems introduce the requirements for their availability, confidentiality and integrity properties. These properties are attained by appropriate mechanisms, including cryptographic protocols and countermeasures against known threats such as Denial of Service attacks. To cope with the problems associated with concurrency and communication, the programmers rely on protocols and algorithms that provide high-level safety guarantees for the computations, such as atomicity, information consistency, isolation, fault tolerance and various domain-specific correctness properties. We have developed automated verification and validation techniques for the security of cryptographic protocols and various attack countermeasures, and for the safety of systems that rely on complex concurrency and communication mechanisms. These techniques take advantage of recent advances in the areas of model checking and correctness-by-construction. Our primary aim is to mitigate the inherent problems of state explosion and property preservation between the system's design and implementation. The proposed analyses concern both qualitative and quantitative system properties.
17 Mar 2014 at 10:00 - "Deploying defeasible logics in the Semantic Web"
Speaker:
Dr Stratos Kontopoulos,
Informatics and Telematics Institute (ITI) of the Center for Research and Technology, Hellas (CERTH), Greece
Abstract:
Defeasible logics are a member of the non-monotonic logics family that allows reasoning with incomplete and conflicting information. When compared to more mainstream non-monotonic reasoning approaches, the main advantages of defeasible reasoning are enhanced representational capabilities and low computational complexity. Since the Web comprises a drastically dynamic environment, defeasible logics can constitute a very suitable and valuable knowledge representation tool. The presentation will give a brief overview of defeasible logics and will study modern defeasible logics applications in the Semantic Web.

25 Feb 2014 at 14:00 - "Smart Cyber Physical Systems"
Speaker:
Dr Athanasia Tsertou,
Institute of Communication and Computer Systems, Athens, Greece
Abstract:
Increased penetration of the Internet of Things (IoT) concept in various domains of everyday life as well as rapid advances in miniaturization, speed, mobility and power conservation have led to the inherent need of combining the pervasive use of information and communication technologies with elements of the physical world. Tightly coupled cyber and physical systems that exhibit an increased level of integrated intelligence are referred to as Cyber Physical Systems (CPS). CPS go one step further from embedded devices and may be viewed essentially as a network of interacting elements with physical input and output instead of as standalone devices. Applications of CPS include but are not limited to the following: automotive applications, smart energy grid services, wireless body area networks with robotic elements and many more.

16 Dec 2013 at 13:30 - "Information Systems and Internal Control"
Speaker:
Panagiotis Droukas,
Information Systems Auditor at the Bank of Greece
Abstract:
The talk of Mr Droukas will refer to real cyber attacks, like the recent hacking of the electronic subscription system of the Greek Ministry of Health. Depending on each case, Mr Droukas will present the gaps that intruders exploit and will highlight the necessity of security check mechanisms.
29 Oct 2013 at 13:00 - "DTN LEO Satellite Communications through Ground Stations and GEO Relays: CGR effectiveness and limits."
Speaker:
Prof. Carlo Caini,
Associate Professor of Telecommunications in the Department of Electrical, Electronic and Information Engineering, University of Bologna, Italy
Abstract:
LEO satellites are characterized by intermittent connectivity with their ground stations. Contacts are short and separated by long intervals, which with urgent data can become a critical factor. To solve this problem, the use of GEO satellites as relay has recently been suggested. This solution is appealing, but has some limits, especially with polar orbits, as the link between the LEO satellite and the GEO relay is affected by long disruptions over polar regions. In the talk, we will show that GEO relays are complementary rather than alternative to ground stations, and that the enabling technology for their combined use is DTN (Delay-/Disruption- Tolerant Networking) architecture and CGR (Contact Graph Routing). The experiments carried out to prove that have highlighted the real effectiveness, but also some limits of the present version of CGR. These results will be thoroughly analyzed during the talk, with the aim of stimulating a dialogue with the audience about possible CGR enhancements and cooperative research.

21 May 2013 - "Observations of the urban thermal environment from Space"
Speaker:
Dr. Iphigenia Keramitsoglou,
Associate Researcher at the Institute for Astronomy, Astrophysics, Space Applications and Remote Sensing (IAASARS) of the National Observatory of Athens
Abstract:
Satellite platforms carrying thermal infrared sensors provide continuous monitoring of the Land Surface Temperature (LST) distribution at a spatial resolution ranging from 3-5km to ~100m. The presentation will include an introduction to satellite remote sensing (Earth Observation) and the potential of satellite-derived products for monitoring the urban environment. Following, a suite of advanced methodologies for the study of the thermal urban environment using satellite images that have been developed at the National Observatory of Athens (NOA) will be presented. The first one is the downscaling of geostationary LST imagery down to 1km spatial resolution using advanced regression algorithms. The second approach is the evaluation of heat wave hazard and risk based on the intensity, duration and time lag between consecutive events as well as the vulnerability of the population using fuzzy logic. Finally, as comparison of thermal patterns, most notably Surface Urban Heat Islands (SUHI), across different cities is hampered by the lack of an appropriate methodology to extract and characterize them, an object-based image analysis procedure has been developed allowing for the calculation of several features (e.g., SUHI area extent and intensity) from the original LST maps. Very recent results for Athens, Greece, will be demonstrated. At the end, the scientific contribution of the presenter to the international initiative of Group on Earth Observations will be discussed that will put all the above into context.

14 May 2013 - "Bridging Scales and Paradigms in Natural System Modelling: an introduction to semantic meta-modelling"
Speaker:
Prof. Ferdinando Villa,
Basque Center for Climate Change
Abstract
The greatly increasing amount of data available for scientific investigation is challenging our ability to understand, synthesize and describe the semantics of what these artifacts observe. In recent years, activities such as the Semantic Web have created a renewed interest for evolving unstructured “metadata” into more formal and accurate description of the datasets used in natural sciences and management. Conceptualizations (ontologies) that can help formalizing scientific observations and the ways the observed parts of a system relate to each other have multiplied as their role becomes more important. Such products allow basic integration of independently collected information and provide a branching point for further specification with domain-specific ontologies, enabling semantic validation of the information collected, transferred and created along data paths.
In this address I will take a step towards a higher-level generalization and present a new modeling language aimed to enable multiple-scale, multiple-paradigm, and modular description of systems. The language is based on a formal definition of what scientific observations are, and presents "models" as strategies to observe abstract concepts and produce data that describe them, harmonizing potentially different views of time and space. This formalism, called semantic meta-modeling, offers a uniform and cohesive approach that encompasses data management, storage, querying and many aspects of traditional modeling.

28 June 2012 - "Storage capacity control policies for dynamic networks"
Speaker:
Dr. George Iosifidis,
Department of Computer and Communications Engineering, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece
Abstract:
Despite the recent renewed interest for node storage, it is still a network resource that has not been adequately exploited in network design. Nowadays storage is cheap compared to bandwidth, with decreasing cost and least space and power requirements. It can be used both in small portable devices and in large amounts located at central communication nodes of backbone networks. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to identify possible methods for enhancing the performance of a network in terms of data transfer capability by exploiting the storage capacity of its constituent nodes. Specifically, we ask the following questions: (i) in which ways and how much we can improve the performance of a network by using storage? (ii) Under what conditions is such an improvement realizable? In this talk, we will discuss these questions and try to give some answers.
11 June 2012 - "From NOOTROPIA to NOOWIT: how a model became a product"
Speaker:
Dr Nikolaos Nanas,
Center For Research and Technology, Thessaly
Abstract:
NOOWIT is an online magazine that adapts to a user's personal interests, the social trends and even to the browser's window. It is the result of more than ten years of research and development in the domain of Information Filtering. NOOWIT is based on NOOTROPIA, a biologically-inspired model that can represent a user's (or a group's) multiple interests, it can continuously adapt to changes in them over time and can evaluate any type of information accordingly. It is NOOTROPIA's innovative and advantageous characteristics, including its ability to incorporate a large number of features, its efficiency, its distributed nature and its unique adaptive capabilities, which allowed its practical application for the creation of NOOWIT. However, turning NOOTROPIA into a full fledged web application, ready to serve hundred of thousands of users, has been a long process that involved many years of team work. The talk will focus on the lessons learned and the engineering and design innovations achieved to create a publication platform, with the ambition to have a fundamental impact on the transition from mass media to really personalized, social media.
8 May 2012 - "Extending DTN into Earth: A Survey of System Implementations and Application Domains"
Speaker:
Dr Artemios G. Voyiatzis,
Industrial Systems Institute/RC "Athena"
Abstract
Disruption- and Delay-Tolerant Networking (DTN) is a novel communication paradigm, originally envisioned for extending Internet into space. More than ten years of active research later, DTN becomes an enabling technology for numerous application domains in terrestrial environments and a wide variety of system implementations has emerged. The presentation summarizes recent developments in the field and provides some insights on areas with high potential for future development.
26 Mar 2012 - "Satellite Cardsharing Forensics"
Speaker:
Ioannis Paschos,
-Digital Evidence Examiner
-Police Captain (retired)
-Founder of the Digital Evidence Lab (Hellenic Police)
-CFCE (Computer Forensics Certified Examiner)
-Certified Interpol Trainer
-Court expert on Digital Evidence (Athens Courts)
Abstract
Satellite TV is in our daily life. The underlying schemes have a number of protection mechanisms such as signal encryption for example. These mechanisms require the client to pay the provider in order to subscribe to the services. However, there is a relatively large community that was motivated to debug these services and came up with some really good new products that surprisingly, cost nothing or cost a fraction of the legal subscription. So they engineered a number of ways to accomplish it like card duplicating or card sharing. In the presentation we will discuss those methods, ways to trace them and what evidence can be found by a digital examiner.
29 Nov 2011 - "Moving Objects and Data Streams: Research Problems and Applications"
Speaker:
Prof. Timos Sellis,
Research Center "Athena" and National Technical University of Athens
Abstract
In many applications nowadays there are requirements for data that "flow" continuously (data streams). Examples include fleet management systems, temperature or other measurement monitoring, even monitoring stock prices. Of particular interest due to the large increase of devices that detect location (e.g. GPS) have applications that manage large volumes of data streams with geospatial information. This talk addresses issues of management of a large number of objects in modern such monitoring applications. In such an environment, the presence of ephemeral streams and dynamically changing data, drastically change the way the processing of so-called "continuous queries" is done, so as to provide answers for the position and trajectory of objects.
12 Apr 2011 - "Development of a database of intensively monitored groundwater systems in Australia"
Speaker:
Dr Barry Croke,
Australian National University
Abstract
Two key components of database construction is providing access to the data, and quality assurance of the data going into the database. As part of an Australian Government funded project, the Australian National University is developing a database of information that will be collected at 5 sites. Access to the database will be provided through a web portal, using the Spatial Information Services Stack developed by AuScope, and applied across multiple Australian Goverment agencies and research organisations. The SISS is a comple integrated suite of open source software tools that support spatial data interoperability using OGC/ISO standards. Data imported into the database will be passed through a quality assurance process in order to detect errors. The goal is for this process to be mostly automated, using tools that will improve in performance as more data is processed. The initial funding for the project will run for 3 years, though the database will be maintained for at least an additional 5 years.
31 Mar 2011 - "From space exploration to monitoring, forecasting and control: the case of energetic charged particles"
Speaker:
Ioannis A. Daglis,
Director, Institute for Space Applications & Remote Sensing [1]
Editor for Magnetosphere and Space Plasma Physics, _Annales Geophysicae_ [2]
Abstract
Energetic charged particles were discovered in Geospace – the near-Earth space – right from the beginning of the space era, by both Sputnik-2 and 1958 Alpha (aka Explorer I). Over five decades of space exploration, we have managed to chart the not-at-all-void space around our planet, to understand the complex electromagnetic phenomena induced by the closest and quite variable star – the Sun – and to make the first attempts to forecast space weather. Today we even aspire to control space weather, in order to protect our space technology assets from detrimental effects of severe space weather or from man-made hazards. I will present an overview of Geospace exploration and understanding, with an emphasis on electromagnetic phenomena that involve charged energetic particles, current efforts to monitor and forecast the dynamic Geospace environment and prospects of controlling it. The role of efficient space data dissemination systems (aka space-data routing) will also be addressed.

22 Feb 2011 - "Modelling and Evaluation of CCN-caching Trees"
Speaker:
Ioannis Psaras, Networks and Services Research Lab, UCL
Abstract
Networking Named Content (NNC) was recently proposed as a new networking paradigm to realise Content Centric Networks (CCNs). The new paradigm changes much about the current Internet, from security and content naming and resolution, to caching at routers, and new flow models. In this paper, we study the caching part of the proposed networking paradigm in isolation from the rest of the suggested features. In CCNs, every router caches packets of content and reuses those that are still in the cache, when subsequently requested. In this talk, we model and evaluate this caching feature of CCNs.
Our modelling proceeds both analytically and by simulation. Initially, we develop a mathematical model for a single router, based on continuous time Markov-chains, which assesses the proportion of time a given piece of content is cached. This model is extended to multiple routers with some simple approximations. The mathematical model is complemented by simulations which look at the caching dynamics, at the packet-level, in isolation from the rest of the flow.
Our findings indicate that, as expected, there is a clear network-wide performance gain for popular content, but this gain: i) goes down to almost zero for unpopular content, which is, however, the case most of the times, ii) depends heavily on the size of the router-cache and iii) is different between edge/leaf and core Internet routers.
Paper can be found at: http://www.ee.ucl.ac.uk/~uceeips/ccn-caching-networking11-ipsaras.pdf


22 Dec 2010 - "Resource allocation in mobile networks"
Speaker:
Desislava C. Dimitrova, University of Twente, Netherlands
Abstract
The main purpose of mobile networks is to enable customers that are located at arbitrary geographical locations to communicate with each other without the need of a physical connection. A key element of providing wireless connectivity is the management of the radio spectrum to be shared by the mobile users. The challenge in the spectrum management is to find a trade-off between efficiently using the network and at the same time providing the quality of service (QoS) requested by the users. Scheduling is the resource management mechanisms responsible for the distribution of the available radio resource over the users that have requested service.
This presentation discusses three main topics uplink scheduling schemes in mobile networks (UMTS/EUL and LTE) and the possibilities to adopt relaying as a technique to boost performance. At each discussion point special attention is given to the impact of flow-level dynamics, i.e. the random user behaviour regarding the initiation and completion of data flow transfers. In order to capture the effects of flow dynamics a novel hybrid analysis approach is used. The approach is a combination of analytical methods and simulation. Several numerical results will be discussed in terms of mean flow transfer times and throughputs.
06 Dec 2010 – "Electronic Spam: The approach of a digital evidence analyzer"
Speaker:
Anargyros Chrysanthou,
Inspector at the Hellenic Data Protection Authority
Abstract
Nowadays information technologies, communications and the Internet are rapidly evolving. In this information era citizens can obtain information from the Internet like never before. This vast amount of available information includes dangers that are highly connected to the protection of our personal data. One of these dangers involves citizen's e-mail addresses, which receive spam e-mail everyday.
In this lecture, we will present the general problem of spam, the existing legislation (in national level), as well as legal actions for e-mail marketing. Furthermore, we will analyze the most popular techniques of spammers , both in Greece and worldwide, and we will discuss the challenges a digital evidence analyzer faces during the investigation of a spam complaint from the Hellenic Data Protection Authority. Finally, practical scenarios of spam complaints and their investigation method, as far as digital evidence is concerned, will be presented.
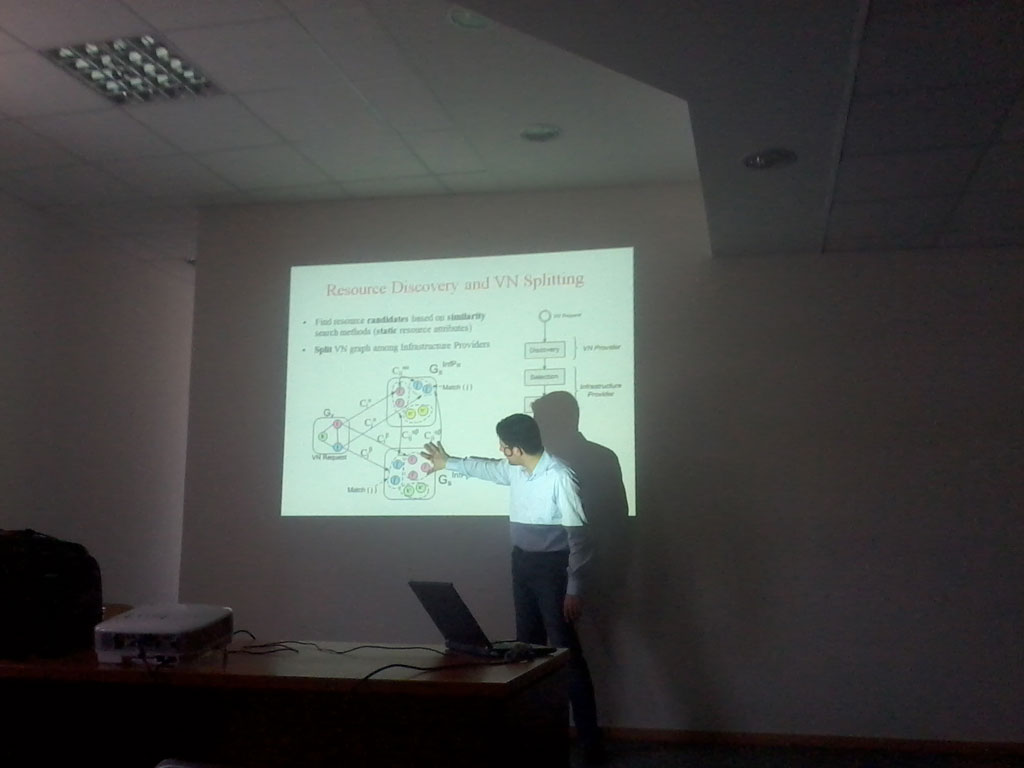
24 Nov 2010 – "Virtual network provisioning and fault-management across mulitple domains", Panagiotis Papadimitriou
Speaker:
Panagiotis Papadimitriou,
Asst. Professor
Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
University of Hannover
Abstract
The tussle between reliability and functionality of the Internet is firmly biased on the side of reliability. New enabling technologies fail to achieve traction across the majority of ISPs. We believe that the greatest challenge is not in finding solutions and improvements to the Internet's many problems, but in how to actually deploy those solutions and re-balance the tussle between reliability and functionality. Network virtualization provides a promising approach to enable the co-existence of innovation and reliability.
To this end, we leverage virtualization to provision virtual networks customized to the requirements of a particular networkcservice. Once allocated, virtual networks will be subject to dynamic variations due to changes in services demands, traffic loads, physical resources and infrastructures, and subject to mobility-induced variations. We propose adaptive provisioning to maintain virtual network topologies, comply with established contracts, expand initial allocations on demand, release resources no longer useful, optimize resource utilisation and respond to anomalies, faults and evolving demands.


























